Endurance Exercise Provides Protection Against the Negative Effects of Stress
-physical activity provides protection against the effects of stress that have been linked to poor cardiorespiratory health -endurance exercise decreases secretion of hormones and neurotransmitters triggered by emotional stress. In conclusion endurance exercise for 3 hours at the intensity of 70HRR increased the plasma antioxidant level and this increase may contribute to inhibit exercise-induced oxidative stress in.
Antioxidants Free Full Text Exercise Induced Oxidative Stress And The Effects Of Antioxidant Intake From A Physiological Viewpoint Html
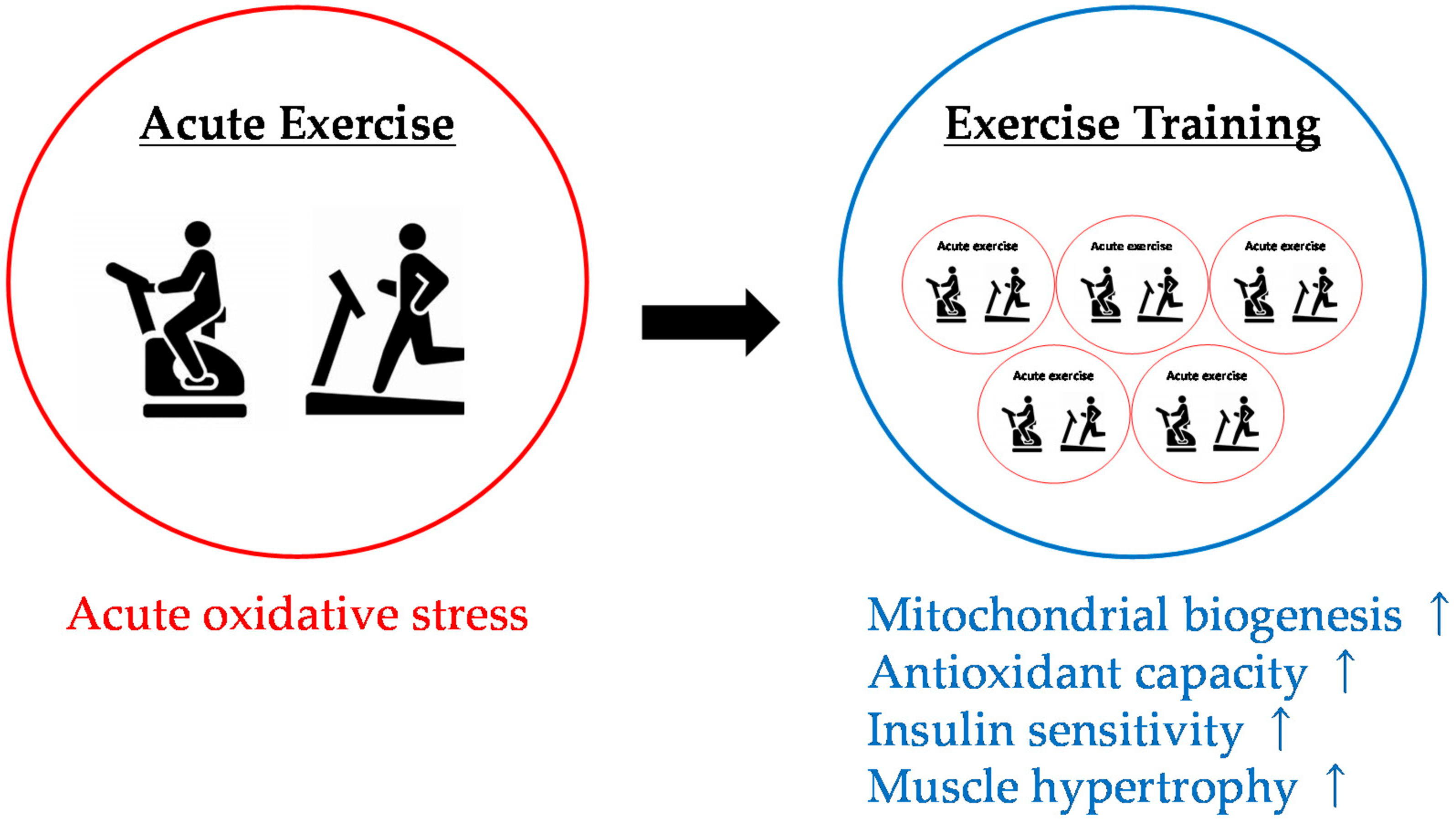
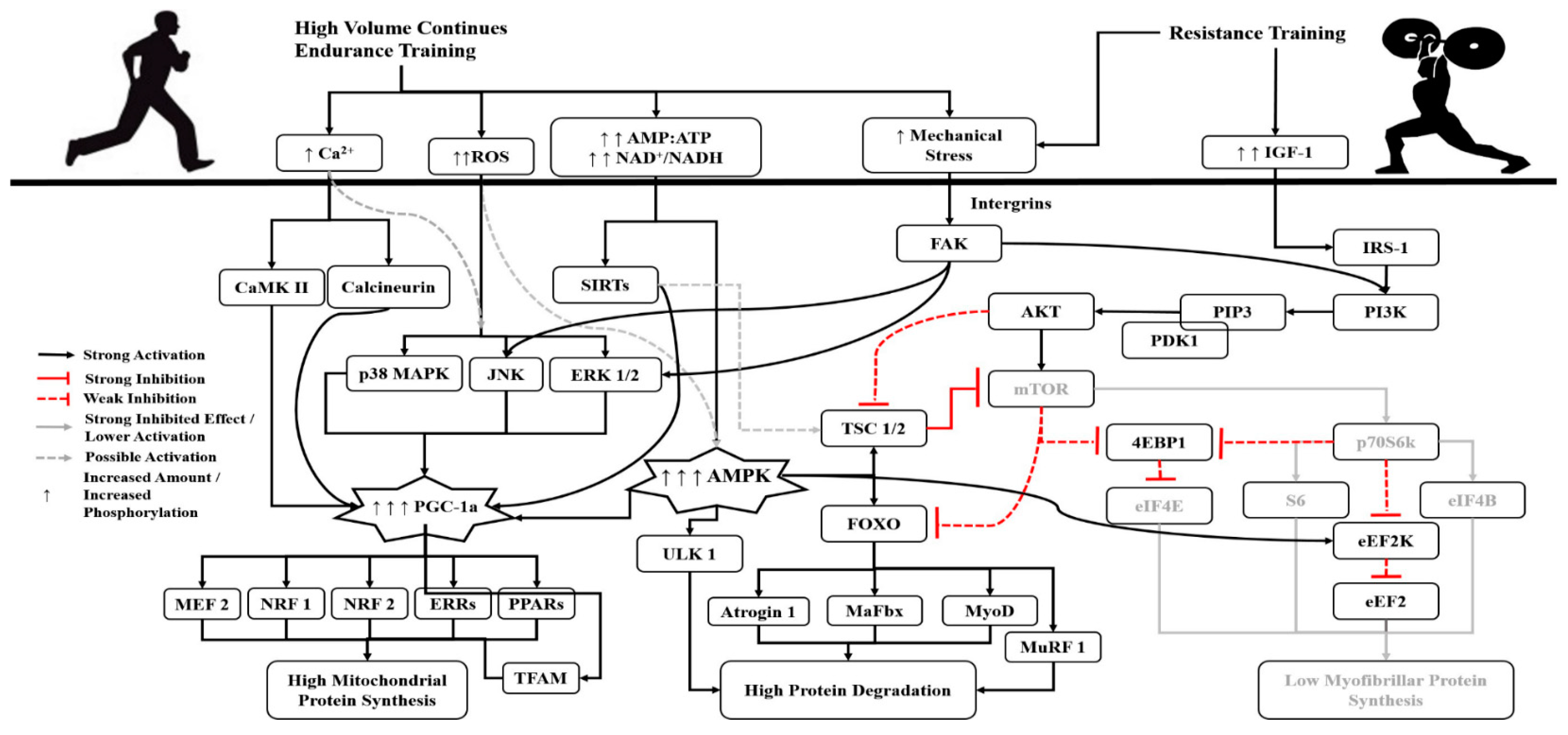
Endurance exercise training imposes oxidative metabolic and heat stress on skeletal muscle which activates a variety of cellular signaling pathways that ultimately leads to the increased expression of proteins that have been.
. Performing physical activities provides proof of skill mastery and self-control thus enhancing self-image. Morinda officinalis How enhances exercise endurance and possesses protective effects against oxidative stress of the rats after exercise August 2010 African Journal of. As the result of regular endurance exercise resting heart rate is often up to 10 beats per minute lower.
Most people who participate in regular endurance exercise experience social psychological and emotional benefits. Emerging evidence suggests that exercise training can provide a level of protection against disuse muscle atrophy. Regular bouts of endurance exercise results in increased endogenous antioxidant enzymes in the trained skeletal muscles.
- Improved psychological and emotional well-being. Endurance exercise training imposes oxidative metabolic and heat stress on skeletal muscle which activates a variety of cellular signaling pathways that ultimately leads to the increased expression of proteins that have been demonstrated to protect muscle. Surprisingly the protective effect is similar after short-term 3 to 5 days and long-term weeks to months exercise training.
A study in the Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology tested the effect of aerobic swimming on rats and found that intense endurance exercise leads to oxidative stress that causes dysfunction in the male reproductive system. Results of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies are more consistent in indicating that aerobic exercise training has antidepressant and anxiolytic effects and protects against harmful consequences of stress. The negative effects of oxidative stress are associated with the pathophysiology of many diseases and aging.
Endurance exercise provides protection against the negative effects of stress. Recreational sports provide the opportunity to socialise have fun and to strive to excel. These experiments tested the hypothesis that short-term exercise training protects against acute DOX-induced muscle toxicity in part due to decreased forkhead-box O FoxO transcription of atrophy genes.
Physical exercise can also increase oxidative stress and cause disruption of redox homeostasis. Exercise enhances ones sense of general well-being. A lot of lower-body strength-training exercises also will improve your balance.
They are the consequence of a reduction in resistance to oxidative stress with aging and the accumulation of free radicals. 404661 In a trial specifically designed to assess the loss of cardioprotective effects after training cessation Lennon et al 62 were able to show a persistence of protection against myocardial stunning for up to 9. Rats n 6 per group were assigned to sedentary or endurance exercise-trained groups and paired with either placebo or DOX treatment.
Also called aerobic exercise endurance exercise includes activities that increase your breathing and heart rate such as. Many different types of exercises can improve strength endurance flexibility and balance. It reduces negative effects of stress.
For example practicing yoga can improve your balance strength and flexibility. Endurance exercise provides protection against the negative effects of stress. Emerging evidence suggests that exercise training can provide a level of protection against disuse muscle atrophy.
True To develop a particular fitness component you must perform exercises. Emerging evidence suggests that exercise training can provide a level of protection against disuse muscle atrophy. The aim of this review is to provide a critical up-to-date review of existing evidence on the immunomodulatory potential of selected.
The main adaptations to endurance exercise include an improvement of mechanical metabolic neuromuscular and contractile functions in muscle2 a rebalance of electrolytes3 a decrease in glycogen storage4 and an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle tissue5 Furthermore endurance exercise has a profound impact on oxidative stress5. Exercise as a protective mechanism against the negative effects of oxidative stress in first-episode psychosis. Brace yourself for the really bad news about intense aerobic exercise.
It reduces negative effects of stress. Provide protection against the damaging effects of free radicals. Exercise can provide stress relief for your body while imitating effects of stress such as the flight or fight response and helping your body and its systems practice working together through those effects.
This translates to an improved ability to protect against exercise-induced oxidative stress in skeletal muscles. Exercise can provide stress relief for your body while imitating effects of stress such as the flight or fight response and helping your body and its systems practice working together through those effects. Many fruits and vegetables contain numerous compounds with antioxidant activity.
Heavily exercising endurance athletes experience extreme physiologic stress which is associated with temporary immunodepression and higher risk of infection particularly upper respiratory tract infections URTI. Which of the following statements about regular exercise and its ability to help manage stress is FALSE. Endurance exercise training imposes oxidative metabolic and heat stress on skeletal muscle which activates a variety of cellular signaling pathways that ultimately leads to the increased expression of proteins that have been demonstrated to protect muscle.
This investigation tested the hypothesis that an IL-6-mediated acute-phase response after exercise provides negative-feedback protection against exercise-induced oxidative stress. Healthy young n 16 264 - 18 yr and older men n 16 711 - 20 yr ran downhill for 45 min at 75 maximal oxygen consumption before and after a 12-wk period of supplementation. The set of physical attributes that allow the body to respond or adapt to the demands and stress of physical effort is physical fitness.

Sports Free Full Text A Brief Review On Concurrent Training From Laboratory To The Field Html
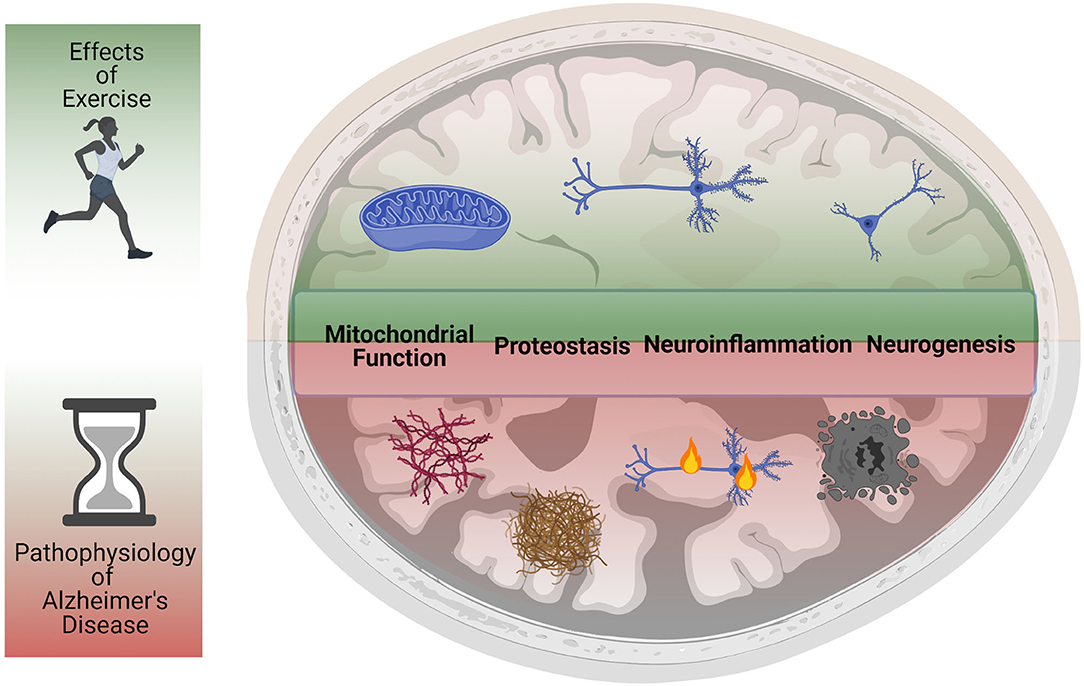
Frontiers Forgot To Exercise Exercise Derived Circulating Myokines In Alzheimer S Disease A Perspective Neurology

Exercise Under Heat Stress Thermoregulation Hydration Performance Implications And Mitigation Strategies Physiological Reviews
0 Response to "Endurance Exercise Provides Protection Against the Negative Effects of Stress"
Post a Comment